Knowledge and Skills Statement
The further explanation is designed to be a resource for educators that helps them better understand the topic their students are learning. Further explanations may be written at a more complex level than would be expected for students at the grade level.
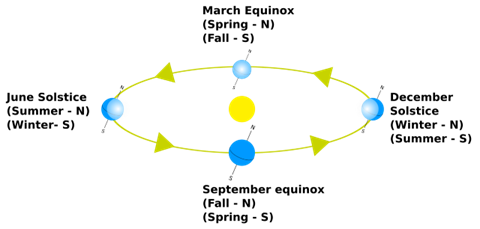
The tilt of Earth's axis and position in orbit around the Sun determine the angle of incidence of sunlight on Earth's surface, causing changes in seasons. Diagrams like the one below may help students understand why locations in the Northern Hemisphere have weather that is different than locations in the Southern Hemisphere. For example, in June the Earth’s tilt exposes the Northern Hemisphere to more direct sunlight, causing summer weather. The Southern Hemisphere has less direct exposure to sunlight, causing winter weather in June. In December, the Earth has revolved to the opposite side of the Sun. The Northern Hemisphere is now exposed to less direct sunlight, causing winter weather. The Southern Hemisphere is now exposed to more direct sunlight, causing summer weather.
Research
Corin, Elysa, and Todd Boyette. “Including Students in a Model of the Earth, Moon, and Sun System." Science Scope 37, no. 9 (Summer 2014): 30–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/43691520.
Summary: In part four of the article, "Including Students in a Model of the Earth, Moon, and Sun System," the movement of the Earth around the sun is directly connected to the change in seasons.