- Science
- Grade 6
- Force, motion, and energy

Knowledge and Skills Statement
The further explanation is designed to be a resource for educators that helps them better understand the topic their students are learning. Further explanations may be written at a more complex level than would be expected for students at the grade level.
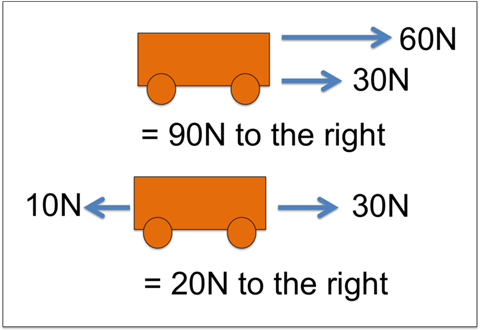
The cart on the top has two arrows to the right of it. The first arrow is assigned a value of 60 N and the second arrow is assigned a value of 30 N. Below the cart, it indicates that adding the two forces together equals 90 N to the right. The cart on the bottom shows an arrow to the left equaling 10 N and an arrow to the right equaling 30 N of force. Below the cart it indicates that adding the two forces together equals 20 N of force to the right.
Qwertyxp2000, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Research
Bobrowsky, Matt. “SCIENCE 101 Background Booster for Elementary Teachers: Q: Does a Force on an Object Always Result in Motion?” Science and Children 57, no. 2 (2019): 77–79. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26901523.
Summary: Forces can be described by their strength and direction. This article assists in understanding the directionality and strength needed for a change in motion and provides examples for classroom use.