- Science
- Grade 3
- Matter and energy
Science.3.6.C
predict, observe, and record changes in the state of matter caused by heating or cooling in a variety of substances such as ice becoming liquid water, condensation forming on the outside of a glass, or liquid water being heated to the point of becoming water vapor (gas); and

Knowledge and Skills Statement
The further explanation is designed to be a resource for educators that helps them better understand the topic their students are learning. Further explanations may be written at a more complex level than would be expected for students at the grade level.
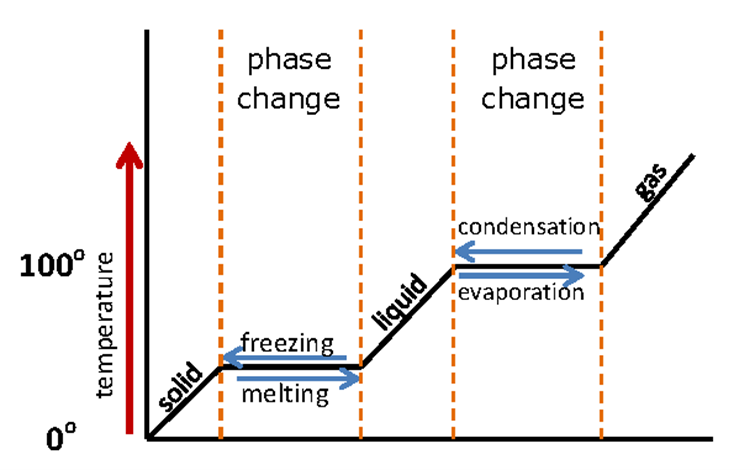
In high school, students will use phase change graphs for specific substances to determine when that substance will change from a solid to a liquid to a gas. See the graph below for an example.
The graph shows temperature as a measurement on the y-axis and the state of matter on the x-axis. As an instructor, it is important to understand that the temperature of a substance is a measure of thermal energy, which can be added to or removed from a substance. The change of state that is observed in a substance is a result of the transfer of thermal energy between objects, or heat. An object feels warm or hot when thermal energy moves from the object into your hand.
A common misconception is that both "cold" and "heat" can move between objects. For example, someone may think that the cold from an ice cube is transferred into their hand when it is actually the heat from their hand moving into and melting the ice. Although plasma is a state of matter, because there is little natural plasma on Earth, it is not relevant to students until they begin discussing atoms and the formation of stars in middle school.
Research
"Bobrowsky, Matt. 2022. “Science 101 Q: What Makes a Great Science Investigation?” Science and Children 59, no. 5 (May/June 2022): 62–65.
https://www.proquest.com/docview/2665176647?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals."
Summary: Moisture in the air is usually a gas called water vapor. This article explains the process of condensation and provides examples of how and when students can observe condensation in everyday life. The author explains that when heat is added to moisture in the air, the gas changes into a liquid, which is condensation. Teachers can add ice to a glass jar and allow students to observe how water forms outside of the jar. Students may have misconceptions about the water, such as believing it came from inside the jar. Teachers should clarify that the water came from the air. One example of condensation that students witness regularly is seeing water in their bathroom mirror after a shower. Teachers should explain to students that vapor hitting the cool mirror causes the water vapor (gas) to change into a liquid.
Research
Siulc, Janet, Marilyn Cook, Ingrid Sherwood, Peggy Ashbrook, Yvonne Fogelman, and Meredith Knight. 2006. “The Early Years: The Matter of Melting.” Science and Children 43, no. 4 (January 2006): 18–21. http://www.jstor.org/stable/43173900.
Summary: Exploring changing states of matter can help students build vocabulary, make predictions, and practice using their senses. The teacher in this article uses children’s books to introduce changing states of matter to students in a way that connects to real-life experiences they have had. Students often have difficulty with the concept of melting unless they can witness it happening. Teachers can have students participate in a hands-on activity to build their understanding of solids melting to become liquids due to temperature change.