Knowledge and Skills Statement
The following is an example of how to assess proficiency of this student expectation (SE) or a portion of the SE.
Provide each student with a different animal picture to glue in their notebooks. Have students label the different structures of their animal. Once students have labeled their pictures, have them find a partner, share their animals, discuss how each animal might use its structures, and trade notebooks. Repeat the mix-pair-share until all students have shared with each other.
Students may explain that animals that have large eyes may be able to see better, allowing them to avoid predators more easily. They may also recognize that a predator that can hear its prey is more likely to catch it. Animals move in different ways, and students should be able to recognize some of the different ways animals move and how that helps them be successful in their environment. For example, birds move with legs or wings, depending on the situation. Fish move with fins, and worms crawl. Each of these movements helps the animal live successfully in their environment.
The further explanation is designed to be a resource for educators that helps them better understand the topic their students are learning. Further explanations may be written at a more complex level than would be expected for students at the grade level.
The structure that allows an animal to see is the eye. Different types of animals have different types of eyes
| Cat | Spider | Octopus |
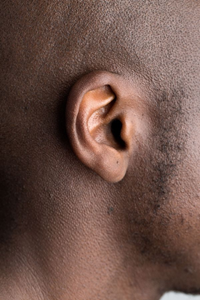
The structure that allows an animal to hear is the ear. Different animals have different ear structures.
| Rabbit | Frog | Human |
Animals have different types of structures that allow them to move, such as hooves, fins, or wings.
| Deer | Cuttlefish | Butterfly |
Animals have different kinds of structures that allow them to grasp objects. These structures can have multiple purposes. For example, dogs use their mouth to eat food and grasp objects.
| Chimpanzee | Elephant | Dog |
Research
Sinoradzki, Kristen, and TJ McKenna. 2021. “What's so Phenomenal about Animals?: Using Structure and Function to Explore Animal Diversity” Science and Children: Global Connections 58, no.6 (July/August 2021): 86-90. https://www.nsta.org/science-and-children/science-and-children-julyaugust-2021-0/whats-so-phenomenal-about-animals.
Summary: This article explains that allowing students to explore animal diversity and the different structures that allow them to survive can help increase student engagement. Discussions about this topic can help promote a broader vocabulary.