- Science
- Grade 3
- Force, motion, and energy

Knowledge and Skills Statement
The further explanation is designed to be a resource for educators that helps them better understand the topic their students are learning. Further explanations may be written at a more complex level than would be expected for students at the grade level.
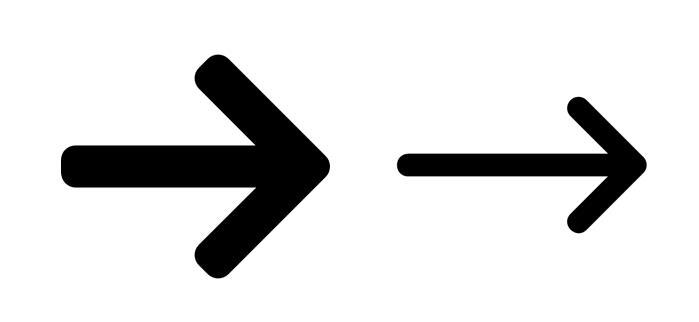
As students describe forces acting on objects, they may indicate the strength and direction of the forces as arrows of varying lengths or thicknesses. The arrows below represent the common conventions used to describe and compare strength of forces in diagrams
Thick (large) arrows represent a stronger force. Thin (small) arrows represent a weaker force.
Thin Arrow: Icon made by Handicon from www.flaticon.com
Research
"Wilcox, Jesse, Naryah, Moore, Sarah Nolting, Courtney Reyna, and Caitlyn. 2021. “Don’t Force It! Using Guiding Questions to Scaffold Kindergartner’s Thinking of Pushes And Pulls.” Science and Children 59, no. 2 (2021): 33-37.
www.nsta.org/science-and-children/science-and-children-novemberdecember-2021/dont-force-it."
Summary: Students have many common misconceptions about magnets. This article addresses these misconceptions and outlines the importance of scaffolding when teaching magnet concepts. Complex ideas about magnets can be difficult for students to comprehend because students cannot see what is happening between a magnet and the object it is attracted to. Students need to know that magnets can attract and repel or push and pull and should be allowed to explore this concept with magnets while teachers ask guiding questions. Allowing students to explore magnets strengthens other important science skills, such as making predictions and categorizing.
Research
"Bobrowsky, Matt. 2019. “SCIENCE 101: Q: What’s Wrong With ‘For Every Action, There Is an Equal and Opposite Reaction’?” Science and Children 56, no. 7, (2019): 69–73.
https://www.proquest.com/docview/2187121325?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals."
Summary: The author of this article explains how forces act on each other. Readers are asked to clap their hands together to see that they feel the same amount of force from each hand and that the forces are equal in strength and opposite in direction. Similarly, magnets can either attract or repel each other, but the forces from each magnet are the same and occur simultaneously. Many students are surprised to learn that when gravity acts on an object, like an apple falling to the ground, the apple also exerts a small gravitational tug on the Earth. Students should know that forces come in pairs. Students can observe a set of blocks stacked on top of each other and try to identify all of the pairs of forces.