Sections
Critical Thinking Questions
Critical Thinking Questions
22.
What are the roles of ATP and NADPH in photosynthesis?
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that produce sugars.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light independent reactions, to be used in the light dependent reactions that produce sugars.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that produce proteins.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that use sugars as reactants.
23.
What is the overall outcome of the light reactions in photosynthesis?
- NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light reactions and are used to power the light independent reactions.
- NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light dependent reactions.
- Sugar and ATP are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light independent reactions.
- Carbon dioxide and NADPH are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light dependent reactions.
24.
How does the equation relate to both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
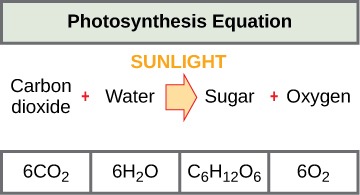
- Photosynthesis utilizes energy to build carbohydrates while cellular respiration metabolizes carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis utilizes energy to metabolize carbohydrates while cellular respiration builds carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both utilize carbon dioxide and water to produce carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both metabolize carbohydrates to produce carbon dioxide and water.
25.
How is the energy from the sun transported within chloroplasts?
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll a molecules that excite an electron, which is then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-II to PS-I. The products of the light dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) I, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll, molecules that excite electrons, which is then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex then transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-II to PS-I. The products of the light dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll molecules that in turn excite electrons, which are then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-I to PS-II. The products of the light dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll molecules that excite electrons, which is then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS II to PS I. The products of the light independent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
26.
Explain why X-rays and ultraviolet light wavelengths are dangerous to living tissues.
- UV and X-rays are high energy waves that penetrate the tissues and damage cells.
- UV and X-rays are low energy waves that penetrate the tissues and damage cells.
- UV and X-rays cannot penetrate tissues and thus damage the cells.
- UV and X-rays can penetrate tissues and thus do not damage the cells.
27.
If a plant were to be exposed to only red light, would photosynthesis be possible?
- Photosynthesis does not take place.
- The rate of photosynthesis increases sharply.
- The rate of photosynthesis decreases drastically.
- The rate of photosynthesis decreases and then increases.
28.
Describe the electron transfer pathway from photosystem II to photosystem I in the light-dependent reactions.
- After splitting water in PSII, high energy electrons are delivered through the chloroplast electron transport chain to PSI.
- After splitting water in PSI, high energy electrons are delivered though the chloroplast electron transport chain to PSII.
- After the photosynthesis reaction, the released products like glucose help in the transfer of electrons from PSII to PSI.
- After the completion of the light dependent reactions, the electrons are transferred from PSII to PSI.
29.
What will happen to a plant leaf that loses CO2 too quickly?
- There will be no effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis will slow down or stop possibly.
- Photosynthesis will increase exponentially.
- Photosynthesis will decrease and then increase.
30.
Carbon, in the form of CO2, must be taken from the atmosphere and attached to an existing organic molecule in the Calvin cycle. Therefore, the carbon is bound to the molecule. The products of the cycle only occur because of the added carbon. What are the products of the Calvin cycle and what is regenerated?
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and RuBP is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and RuBisCO is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is a 3-PGA molecule and glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and oxygen is regenerated.
31.
How do desert plants prevent water loss from the heat, which would compromise photosynthesis?
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by closing stomatal pores during the night
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by opening of stomatal pores during the night
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomatal pores closed at all times
- by bypassing CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomatal pores closed at night
32.
Why are carnivores, such as lions, dependent on photosynthesis to survive?
- because the prey of lions are generally herbivores, which depend on heterotrophs
- because the prey of lions are generally smaller carnivorous animals, which depend on non-photosynthetic organisms
- because the prey of lions are generally herbivores, which depend on autotrophs
- because the prey of lions are generally omnivores, which depend only on autotrophs
33.
Why does it take three turns of the Calvin cycle to produce G3P, the initial product of photosynthesis?
- To fix enough carbon to export one G3P molecule.
- To fix enough oxygen to export one G3P molecule.
- To produce RuBisCO as an end product.
- To produce ATP and NADPH for fixation of G3P.
