The Texas State Literacy Plan (TSLP) includes the implementation of an RTI instructional framework for literacy instruction. The Effective Instructional Framework component of the TSLP course explores the implementation of the RTI framework in detail. This lesson is meant to guide you in planning for that implementation as your team designs and oversees your campus-based data-informed plan for improving literacy instruction.
NOTE: The focus of Part 1 of this lesson is to provide an overview of the basic components of RTI and how it is used as an instructional framework for literacy. You will want to review the Effective Instructional Framework (EIF) lessons of the TSLP for an in-depth description of each RTI components and effective RTI implementation in secondary settings.
As a comprehensive framework for literacy instruction, RTI is being implemented from preschool through high school to help students succeed. The Center on Response to Intervention uses the following definition of RTI:
“Response to intervention integrates assessment and intervention within a multi‐level prevention system to maximize student achievement and reduce behavior problems. With RTI, schools use data to identify students at risk for poor learning outcomes, monitor student progress, provide evidence-based interventions and adjust the intensity and nature of those interventions depending on a student’s responsiveness, and identify students with learning disabilities or other disabilities.” (Center on Response to Intervention, 2016)
The following graphic illustrates the multi-level prevention system. The support provided at each level, or tier, increases in intensity to help students succeed.
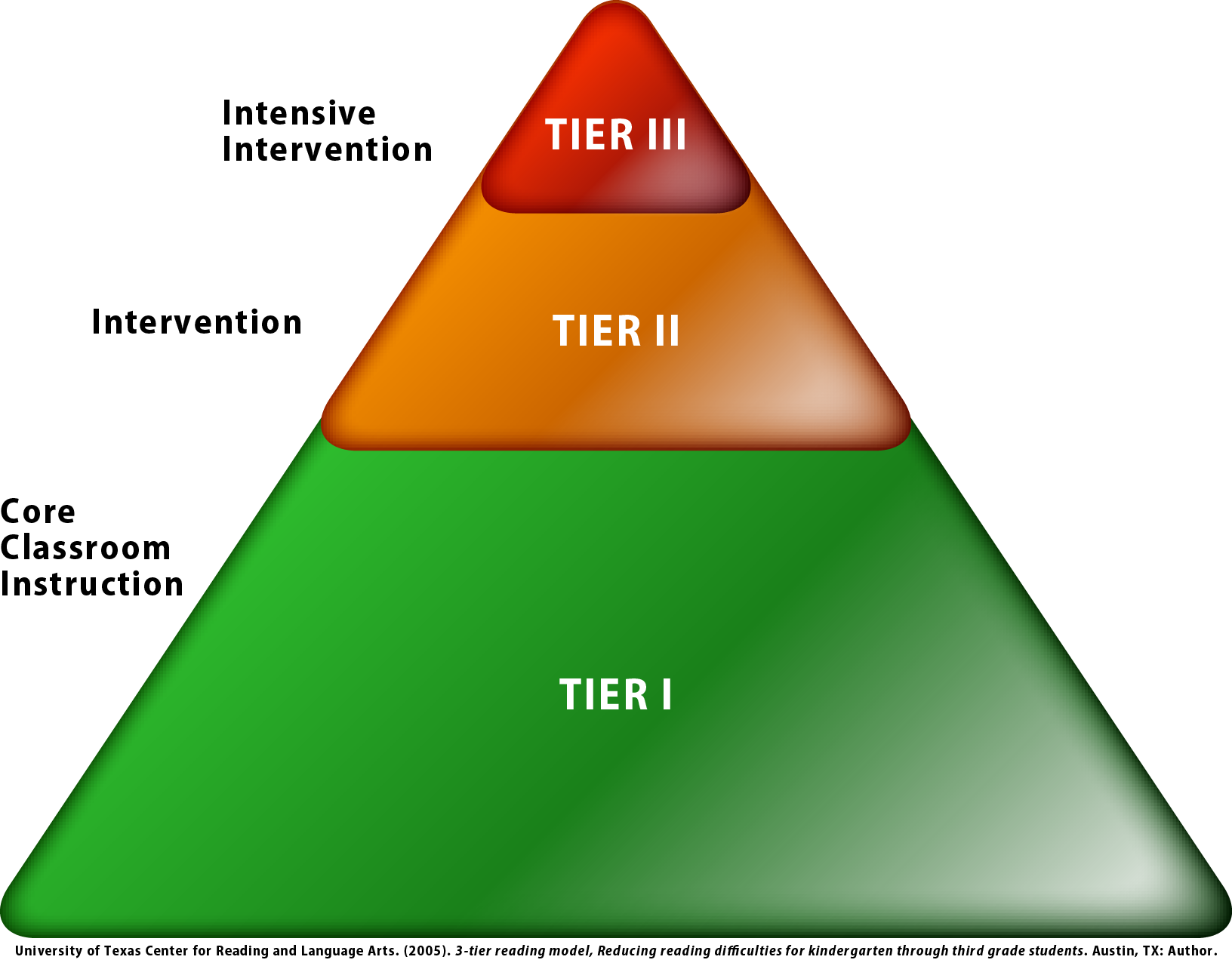
The Center on Response to Intervention (2016) defines the components of RTI as follows:
Screening: Screening is conducted to identify or predict which students may be at-risk for poor learning outcomes. Universal screening tests are typically brief, conducted with all students in a grade level, and followed by additional testing or short-term progress monitoring to corroborate students’ risk status.
Progress monitoring: Progress monitoring is used to assess students’ academic performance, quantify a student rate of improvement or responsiveness to instruction, and evaluate the effectiveness of instruction. Progress monitoring can be implemented with individual students or an entire class.
Multi-level prevention system: A multi-level prevention system includes three levels of intensity or prevention. The primary prevention level includes high-quality, core instruction. The secondary level includes evidence-based intervention(s) of moderate intensity. The tertiary prevention level includes individualized intervention(s) of increased intensity for students who show minimal response to secondary prevention. (See graphic above.)
Data-based decision making: Data analysis and decision making occur at all levels of RTI implementation, at all levels of instruction, at all levels of movement within the multi-level prevention system, and regardless of disability identification (in accordance with state law).
Read an example of how your team might implement RTI at your campus.
Scenario: The campus-based leadership team at X Middle School is ready to begin planning for RTI implementation. Team members know they must assess their current needs and make decisions about how to implement the following components of RTI: screening, progress monitoring, core instruction, intervention instruction, and data-based decision making.
Team members decide to initiate the following action plan to guide their steps in RTI implementation:
Proposed Action Plan
- Assess the current needs of the school.
- Determine which components of RTI are already in place (e.g., screening measures) and identify school resources and potential barriers to implementation (e.g. school schedule).
- Clearly define implementation goals.
- Identify the campus-based leadership team members and other staff best suited to lead implementation for each component of RTI.
- Establish a timeline for implementation.
- Establish intervention schedules that do not interfere with students’ core instructional time.
- Identify and train coaches to assist teachers with implementation.
- Plan professional development for staff.
The first proposed steps for the action plan are to assess the current needs of the school and inventory which components of RTI are already in place. The campus-based leadership team decides to review the student-level data to determine which students need support and to use the components of RTI that are already in place to develop a plan for implementation.
Once the team articulates the implementation goals and identifies the staff who will lead the implementation process, realistic timelines are set to ensure that everyone adheres to the implementation process. Next, the team identifies leadership team members and other staff who will train coaches and plan professional development. (Note that these duties may be delegated to staff who are not on the campus-based leadership team.) Once the action plan is in effect, the leadership team begins implementation.

TO LEARN MORE: Click on the links below to see a list of useful resources for RTI implementation.
The “Essential Components of RTI—A Closer Look at Response to Intervention” from the Center on Response to Intervention provides a definition of RTI, reviews essential RTI components (screening, progress monitoring, the multilevel prevention system, and data-based decision making), and responds to frequently asked questions about implementing RTI.
Helpful documents from the High School Tiered Interventions Initiative (HSTII), a collaboration of the National High School Center, the Center on Response to Intervention, and the Center on Instruction, include the following:

NEXT STEPS: Depending on your team’s progress in implementing RTI, you may want to consider the following next steps:
- Review the resources listed above in To Learn More, especially the examples relevant to your campus grade range.
- Examine your current practice to determine which components of RTI have already been implemented at your campus.
- Determine what specific elements you will look for in each RTI component and, for those elements, how you will evaluate the current level of effective implementation (e.g., What does Tier I instruction include? Tier II? Tier III?).
- Determine ways to communicate with teachers, parents and families, and other stakeholders regarding the model.
- Establish timelines and procedures for examining the impact of intervention instruction on student literacy achievement.

