Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
In this section, you will explore the following questions:
- How do plants absorb energy from sunlight?
- What are the differences between short and long wavelengths of light? What wavelengths are used in photosynthesis?
- How and where does photosynthesis occur within a plant?
Connection for AP® Courses
Connection for AP® Courses
Photosynthesis consists of two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions or Calvin cycle. The light-dependent reactions occur when light is available. The overall equation for photosynthesis shows that is it a redox reaction; carbon dioxide is reduced and water is oxidized to produce oxygen.
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, whereas the Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. Embedded in the thylakoid membranes are two photosystems (PSI and PSII), which are complexes of pigments that capture solar energy. Chlorophylls a and b absorb violet, blue, and red wavelengths from the visible light spectrum and reflect green. The carotenoid pigments absorb violet-blue-green light and reflect yellow-to-orange light. Environmental factors such as day length and temperature influence which pigments predominant at certain times of the year. Although the two photosystems run simultaneously, it is easier to explore them separately. Let’s begin with photosystem II.
A photon of light strikes the antenna pigments of PSII to initiate photosynthesis. In the noncyclic pathway, PSII captures photons at a slightly higher energy level than PSI. (Remember that shorter wavelengths of light carry more energy.) The absorbed energy travels to the reaction center of the antenna pigment that contains chlorophyll a and boosts chlorophyll a electrons to a higher energy level. The electrons are accepted by a primary electron acceptor protein and then pass to the electron transport chain also embedded in the thylakoid membrane. The energy absorbed in PSII is enough to oxidize (split) water, releasing oxygen into the atmosphere; the electrons released from the oxidation of water replace the electrons that were boosted from the reaction center chlorophyll. As the electrons from the reaction center chlorophyll pass through the series of electron carrier proteins, hydrogen ions (H+) are pumped across the membrane via chemiosmosis into the interior of the thylakoid. If this sounds familiar, it should. We studied chemiosmosis in our exploration of cellular respiration in Cellular Respiration. This action builds up a high concentration of H+ ions, and as they flow through ATP synthase, molecules of ATP are formed. These molecules of ATP will be used to provide free energy for the synthesis of carbohydrate in the Calvin cycle, the second stage of photosynthesis. The electron transport chain connects PSII and PSI. Similar to the events occurring in PSII, this second photosystem absorbs a second photon of light, resulting in the formation of a molecule of NADPH from NADP+. The energy carried in NADPH also is used to power the chemical reactions of the Calvin cycle.
Information presented and the examples highlighted in the section support concepts and learning objectives outlined in Big Idea 2 of the AP® Biology Curriculum Framework, as shown in the table. The learning objectives listed in the Curriculum Framework provide a transparent foundation for the AP® Biology course, an inquiry-based laboratory experience, instructional activities, and AP® exam questions. A learning objective merges required content with one or more of the seven science practices.
| Big Idea 2 | Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. |
| Enduring Understanding 2.A | Growth, reproduction and maintenance of living systems require free energy and matter. |
| Essential Knowledge | 2.A.2 The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in eukaryotes involve a series of reactions that capture free energy present in light. |
| Science Practice | 1.4 The student can use representations and models to analyze situations or solve problems qualitatively and quantitatively. |
| Science Practice | 3.1 The student can pose scientific questions. |
| Learning Objective | 2.4 The student is able to use representations to pose scientific questions about what mechanisms and structural features allow organisms to capture, store, and use free energy. |
| Essential Knowledge | 2.A.2 The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in eukaryotes involve a series of reactions that capture free energy present in light. |
| Science Practice | 6.2 The student can construct explanations of phenomena based on evidence produced through scientific practices. |
| Learning Objective | 2.5 The student is able to construct explanations of the mechanisms and structural features of cells that allow organisms to capture, store, or use free energy. |
| Big Idea 4 | Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. |
| Enduring Understanding 4.A | Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. |
| Essential Knowledge | 4.A.2 Chloroplasts are specialized organelles that capture energy through photosynthesis. |
| Science Practice | 6.4 The student can make claims and predictions about natural phenomena based on scientific theories and models. |
| Learning Objective | 4.4 The student is able to make a prediction about the interactions of subcellular organelles. |
| Essential Knowledge | 4.A.2 Chloroplasts are specialized organelles that capture energy through photosynthesis. |
| Science Practice | 6.2 The student can construct explanations of phenomena based on evidence produced through scientific practices. |
| Learning Objective | 4.5 The student is able to construct explanations based on scientific evidence as to how interactions of subcellular structures provide essential functions. |
| Essential Knowledge | 4.A.2 Chloroplasts are specialized organelles that capture energy through photosynthesis. |
| Science Practice | 1.4 The student can use representations and models to analyze situations or solve problems qualitatively and quantitatively. |
| Learning Objective | 4.6 The student is able to use representations and models to analyze situations qualitatively to describe how interactions of subcellular structures, which possess specialized functions, provide essential functions. |
The Science Practices Assessment Ancillary contains additional test questions for this section that will help you prepare for the AP exam. These questions address the following standards:
- [APLO 2.5]
- [APLO 2.16]
- [APLO 2.18]
- [APLO 1.9]
- [APLO 1.32]
- [APLO 4.14]
- [APLO 2.2]
- [APLO 2.3]
- [APLO 2.23]
- [APLO 1.15]
- [APLO 1.29]
How can light be used to make food? When a person turns on a lamp, electrical energy becomes light energy. Like all other forms of kinetic energy, light can travel, change form, and be harnessed to do work. In the case of photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which photoautotrophs use to build carbohydrate molecules (Figure 8.9). However, autotrophs only use a few specific components of sunlight.
What Is Light Energy?
What Is Light Energy?
The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation (solar energy). Humans can see only a fraction of this energy, which portion is therefore referred to as visible light. The manner in which solar energy travels is described as waves. Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength, the distance between consecutive points of a wave. A single wave is measured from two consecutive points, such as from crest to crest or from trough to trough (Figure 8.10).
Visible light constitutes only one of many types of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the sun and other stars. Scientists differentiate the various types of radiant energy from the sun within the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of radiation (Figure 8.11). The difference between wavelengths relates to the amount of energy carried by them.
Each type of electromagnetic radiation travels at a particular wavelength. The longer the wavelength, or the more stretched out it appears in the diagram, the less energy is carried. Short, tight waves carry the most energy. This may seem illogical, but think of it in terms of moving a heavy rope. It takes little effort by a person to move a rope in long, wide waves. To make a rope move in short, tight waves, a person would need to apply significantly more energy.
The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 8.11) shows several types of electromagnetic radiation originating from the sun, including X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) rays. The higher-energy waves can penetrate tissues and damage cells and DNA, explaining why both X-rays and UV rays can be harmful to living organisms.
Absorption of Light
Absorption of Light
Light energy initiates the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb the light. Organic pigments, whether in the human retina or the chloroplast thylakoid, have a narrow range of energy levels that they can absorb. Energy levels lower than those represented by red light are insufficient to raise an orbital electron to a populatable, excited (quantum) state. Energy levels higher than those in blue light will physically tear the molecules apart, called bleaching. So retinal pigments can only see (absorb) 700-400 nm light, which is therefore called visible light. For the same reasons, plants pigment molecules absorb only light in the wavelength range of 700-400 nm; plant physiologists refer to this range for plants as photosynthetically active radiation.
The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal the colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum shows the rainbow of colors, with violet and blue having shorter wavelengths, and therefore higher energy. At the other end of the spectrum toward red, the wavelengths are longer and have lower energy (Figure 8.12).
Understanding Pigments
Understanding Pigments
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each has evolved to absorb only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect or transmit the wavelengths they cannot absorb, making them appear in the corresponding color.
Chlorophylls and carotenoids are the two major classes of photosynthetic pigments found in plants and algae; each class has multiple types of pigment molecules. There are five major chlorophylls: a, b, c and d and a related molecule found in prokaryotes called bacteriochlorophyll. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are found in higher plant chloroplasts and will be the focus of the following discussion.
With dozens of different forms, carotenoids are a much larger group of pigments. The carotenoids found in fruit—such as the red of tomato (lycopene), the yellow of corn seeds (zeaxanthin), or the orange of an orange peel (β-carotene)—are used as advertisements to attract seed dispersers. In photosynthesis, carotenoids function as photosynthetic pigments that are very efficient molecules for the disposal of excess energy. When a leaf is exposed to full sun, the light-dependent reactions are required to process an enormous amount of energy; if that energy is not handled properly, it can do significant damage. Therefore, many carotenoids reside in the thylakoid membrane, absorb excess energy, and safely dissipate that energy as heat.
Each type of pigment can be identified by the specific pattern of wavelengths it absorbs from visible light, which is the absorption spectrum. The graph in Figure 8.13 shows the absorption spectra for chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and a type of carotenoid pigment called β-carotene (which absorbs blue and green light). Notice how each pigment has a distinct set of peaks and troughs, revealing a highly specific pattern of absorption. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not green. Because green is reflected or transmitted, chlorophyll appears green. Carotenoids absorb in the short-wavelength blue region, and reflect the longer yellow, red, and orange wavelengths.
Many photosynthetic organisms have a mixture of pigments; when using them, the organism can absorb energy from a wider range of wavelengths. Not all photosynthetic organisms have full access to sunlight. Some organisms grow underwater where light intensity and quality decrease and change with depth. Other organisms grow in competition for light. Plants on the rainforest floor must be able to absorb any bit of light that comes through, because the taller trees absorb most of the sunlight and scatter the remaining solar radiation (Figure 8.14).
When studying a photosynthetic organism, scientists can determine the types of pigments present by generating absorption spectra. An instrument called a spectrophotometer can differentiate which wavelengths of light a substance can absorb. Spectrophotometers measure transmitted light and compute from it the absorption. By extracting pigments from leaves and placing these samples into a spectrophotometer, scientists can identify which wavelengths of light an organism can absorb. Additional methods for the identification of plant pigments include various types of chromatography that separate the pigments by their relative affinities to solid and mobile phases.
How Light-dependent Reactions Work
How Light-dependent Reactions Work
The overall function of light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. This chemical energy supports the light-independent reactions and fuels the assembly of sugar molecules. The light-dependent reactions are depicted in Figure 8.15. Protein complexes and pigment molecules work together to produce NADPH and ATP.
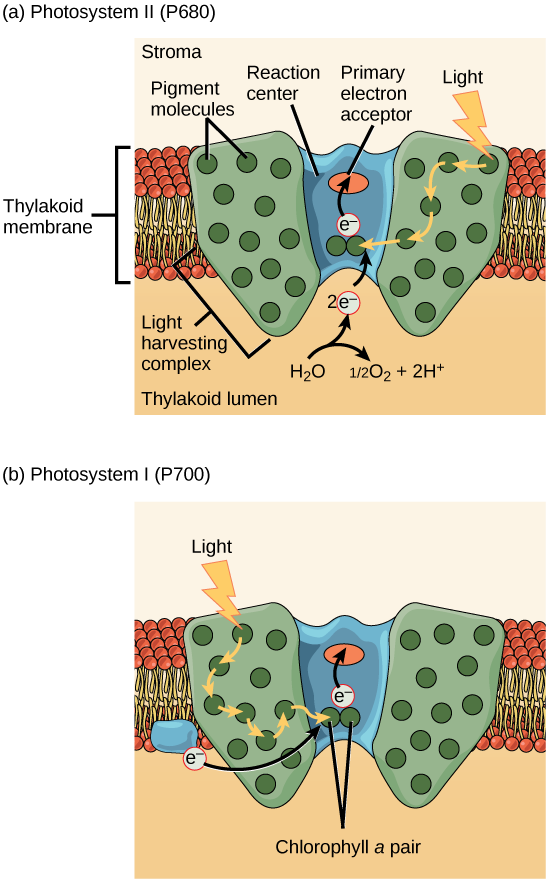
The actual step that converts light energy into chemical energy takes place in a multiprotein complex called a photosystem. There are two types of photosystems found in the thylakoid membrane: photosystem II (PSII) and photosystem I (PSI) (Figure 8.16). The two complexes differ on the basis of what they oxidize; that is, the source of the low-energy electron supply and what they reduce (the place to which they deliver their energized electrons).
Both photosystems have the same basic structure; a number of antenna proteins to which the chlorophyll molecules are bound surround the reaction center where the photochemistry takes place. Each photosystem is serviced by the light-harvesting complex, which passes energy from sunlight to the reaction center; it consists of multiple antenna proteins that contain a mixture of 300–400 chlorophyll a and b molecules as well as other pigments like carotenoids. The absorption of a single photon or distinct quantity or packet of light by any of the chlorophylls pushes that molecule into an excited state. In short, the light energy has now been captured by biological molecules but is not stored in any useful form yet. The energy is transferred from chlorophyll to chlorophyll until eventually, after about a millionth of a second, it is delivered to the reaction center. Up to this point, only energy has been transferred between molecules, not electrons.
Visual Connection
- carbon dioxide
- NADPH
- oxygen
- water
The reaction center contains a pair of chlorophyll a molecules with a special property. Those two chlorophylls can undergo oxidation upon excitation; they can actually give up an electron in a process called a photoact. It is at this step in the reaction center, this step in photosynthesis, that light energy is converted into an excited electron. All of the subsequent steps involve getting that electron onto the energy carrier NADPH for delivery to the Calvin cycle where the electron is deposited onto carbon for long-term storage in the form of a carbohydrate. PSII and PSI are two major components of the photosynthetic electron transport chain, which also includes the cytochrome complex. The cytochrome complex, an enzyme composed of two protein complexes, transfers the electrons from the carrier molecule plastoquinone (Pq) to the protein plastocyanin (Pc), thus enabling both the transfer of protons across the thylakoid membrane and the transfer of electrons from PSII to PSI.
The reaction center of PSII, called P680, delivers its high-energy electrons, one at the time, to the primary electron acceptor, and through the electron transport chain (Pq to cytochrome complex to plastocyanine) to PSI. P680’s missing electron is replaced by extracting a low-energy electron from water; thus, water is split and PSII is re-reduced after every photoact. Splitting one H2O molecule releases two electrons, two hydrogen atoms, and one atom of oxygen. Splitting two molecules is required to form one molecule of diatomic O2 gas. About 10 percent of the oxygen is used by mitochondria in the leaf to support oxidative phosphorylation. The remainder escapes to the atmosphere where it is used by aerobic organisms to support respiration.
As electrons move through the proteins that reside between PSII and PSI, they lose energy. That energy is used to move hydrogen atoms from the stromal side of the membrane to the thylakoid lumen. Those hydrogen atoms, plus the ones produced by splitting water, accumulate in the thylakoid lumen and will be used to synthesize ATP in a later step. Because the electrons have lost energy prior to their arrival at PSI, they must be re-energized by PSI, hence, another photon is absorbed by the PSI antenna. That energy is relayed to the PSI reaction center, called P700. P700 is oxidized and sends a high-energy electron to NADP+ to form NADPH. Thus, PSII captures the energy to create proton gradients to make ATP, and PSI captures the energy to reduce NADP+ into NADPH. The two photosystems work in concert, in part, to guarantee that the production of NADPH will roughly equal the production of ATP. Other mechanisms exist to fine tune that ratio to exactly match the chloroplast’s constantly changing energy needs.
Generating an Energy Carrier: ATP
Generating an Energy Carrier: ATP
As in the intermembrane space of the mitochondria during cellular respiration, the buildup of hydrogen ions inside the thylakoid lumen creates a concentration gradient. The passive diffusion of hydrogen ions from high concentration in the thylakoid lumen, to low concentration in the stroma, is harnessed to create ATP, just as in the electron transport chain of cellular respiration. The ions build up energy because of diffusion and because they all have the same electrical charge, repelling each other.
To release this energy, hydrogen ions will rush through any opening, similar to water jetting through a hole in a dam. In the thylakoid, that opening is a passage through a specialized protein channel called the ATP synthase. The energy released by the hydrogen ion stream allows ATP synthase to attach a third phosphate group to ADP, which forms a molecule of ATP (Figure 8.16). The flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis because the ions move from an area of high to an area of low concentration through a semi-permeable structure.
Link to Learning
Visit this site and click through the animation to view the process of photosynthesis within a leaf.
What role do electrons play in the formation of NADPH?
- Electrons from PSI cause the reduction of NADPH to NADP+.
- Electrons from PSII cause the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH.
- Electrons from PSI cause the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH.
- Electrons are gained which causes the oxidation of NADP+.
Everyday Connection for AP® Courses
If the stomata were sealed, what would happen to oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in a photosynthesizing leaf?
- levels would increase and levels would decrease.
- levels would increase and levels would decrease.
- and levels would both decrease.
- and levels would both increase.
Science Practice Connection for AP® Courses
Think About It
On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata to conserve water. Predict the impact of this on photosynthesis and justify your prediction.
Disclaimer
This section may include links to websites that contain links to articles on unrelated topics. See the preface for more information.